Jun 25, 2025
Ball valves play a critical role in controlling fluid flow within pipelines across various industries. Ensuring their reliability and durability requires thorough testing processes that assess performance under different conditions. This article outlines common ball valve testing procedures and highlights key metrics that manufacturers and users should consider. Additionally, it discusses the use of specialized equipment such as Valve Strength Test Bench and Valve Component Test Bench, which are essential tools in the valve testing process.
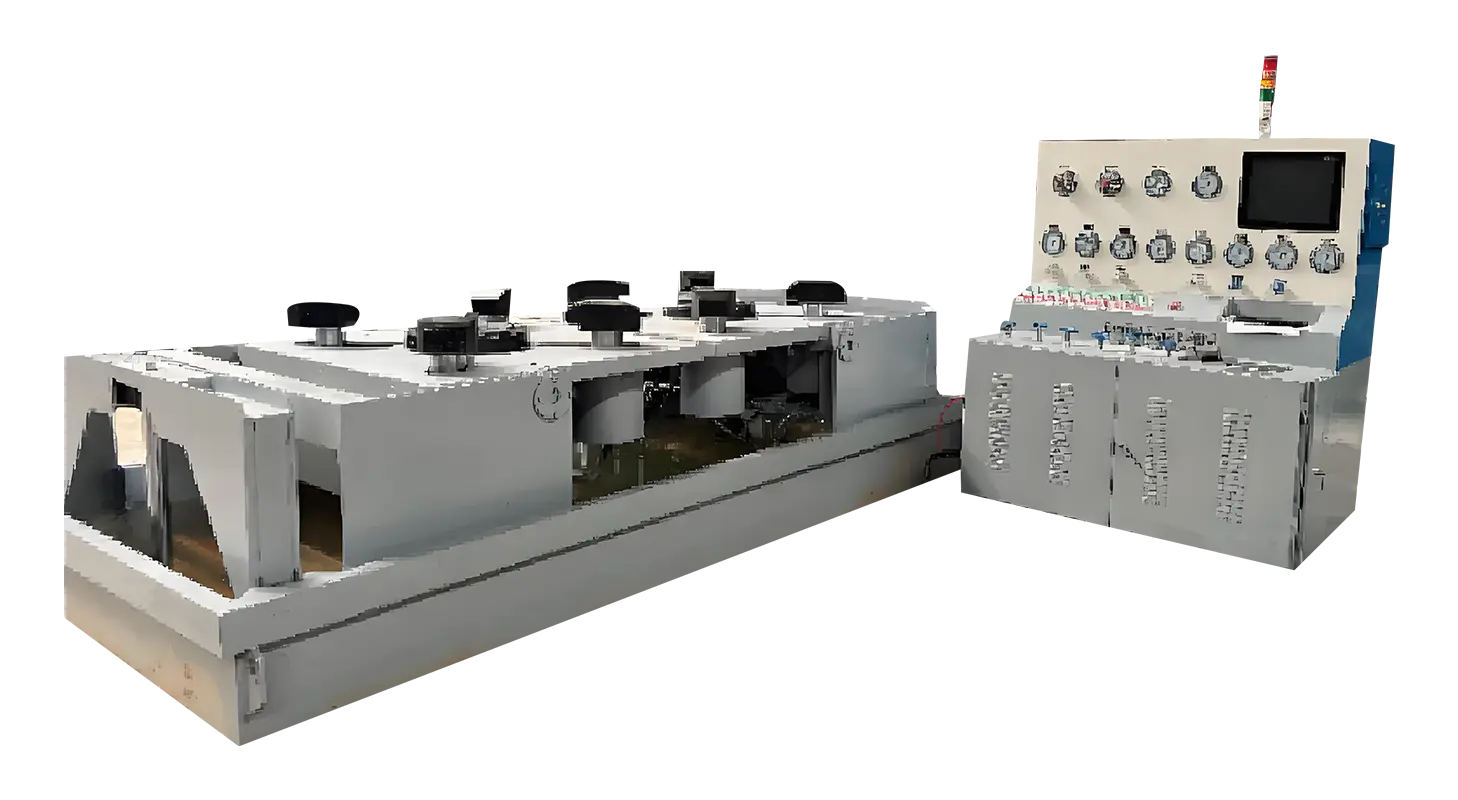
Ball Valve Testing Procedures
Testing a ball valve involves several steps to verify its functionality, pressure resistance, and leakage characteristics. The procedures can vary depending on the valve type and the industry standards applicable, but commonly include the following:
Visual and Dimensional Inspection
Before functional testing, the valve undergoes a visual inspection to identify any manufacturing defects or damages. Dimensional checks ensure that the valve meets design specifications, which is critical for compatibility in piping systems.
Pressure Strength Test
One of the main procedures involves testing the valve’s strength to withstand internal pressures without deformation or failure. This is typically done using a Valve Strength Test Bench. The valve is subjected to pressures higher than its rated working pressure to simulate bad conditions and ensure it maintains integrity.
Leakage Test
Leakage tests are performed to confirm that the valve seals properly and prevent fluid flow when closed. This involves pressurizing the valve and monitoring for leaks through the valve body, seat, or stem packing. Both shell leakage and seat leakage tests are standard, with the valve either fully closed or in partial positions to assess sealing under various operating states.
Functional Testing
Functional tests ensure the valve operates smoothly and correctly. This includes opening and closing the valve multiple times to verify the ease of operation, actuator performance (if applicable), and consistency in valve movement. Functional testing can be performed on a Valve Component Test Bench, which allows individual valve parts to be tested separately.
Torque Testing
Measuring the torque required to operate the valve is another important step. Torque testing helps determine if the valve operates within acceptable limits and identifies any issues such as excessive friction or mechanical binding.
Cycle Testing
Repeated opening and closing cycles simulate long-term use and reveal potential wear or failure points. Cycle testing is essential for understanding valve durability and service life.
Key Metrics in Ball Valve Testing
During and after the testing procedures, several key metrics are measured to evaluate valve performance:
Pressure Rating: The up to pressure the valve can handle safely, verified during the strength test.
Leakage Rate: The volume of fluid passing through the valve seat or body during leakage testing, typically measured in standard units such as ml/min.
Torque Values: The operational torque required for valve movement, crucial for actuator sizing and manual operation.
Cycle Count: Number of successful operating cycles completed without failure.
Response Time: Time taken for the valve to fully open or close, relevant for automated systems.
These metrics provide valuable insights into valve quality and suitability for specific applications.
The Role of Valve Strength Test Bench
A Valve Strength Test Bench is specialized equipment designed to apply controlled pressures to valves, including ball valves, in order to assess their mechanical strength and structural integrity. It provides a safe and repeatable environment for pressure testing by securely mounting the valve and applying hydraulic or pneumatic pressure.
The bench is equipped with pressure sensors, safety valves, and data acquisition systems to monitor the test conditions precisely. By using a valve strength test bench, manufacturers ensure that valves comply with industry pressure standards and can withstand operational stresses during service.
Importance of Valve Component Test Bench
While overall valve testing is critical, individual components such as seats, seals, stems, and actuators also require separate evaluation. A Valve Component Test Bench allows detailed examination of these parts under simulated conditions.
Testing components individually helps in early detection of manufacturing defects or material weaknesses, improving overall valve reliability. For example, seat materials can be tested for wear resistance and sealing ability, while actuators can be evaluated for force and response accuracy.
Ball valve testing procedures encompass multiple steps aimed at verifying strength, functionality, and sealing performance. The use of specialized equipment like the Valve Strength Test Bench and Valve Component Test Bench plays a vital role in these assessments, providing controlled environments for pressure and component testing. By focusing on key metrics such as pressure rating, leakage rate, torque, and cycle durability, manufacturers can ensure that ball valves meet necessary standards and perform reliably in their intended applications. Proper testing supports safety, efficiency, and longevity in fluid control systems across diverse industries.